





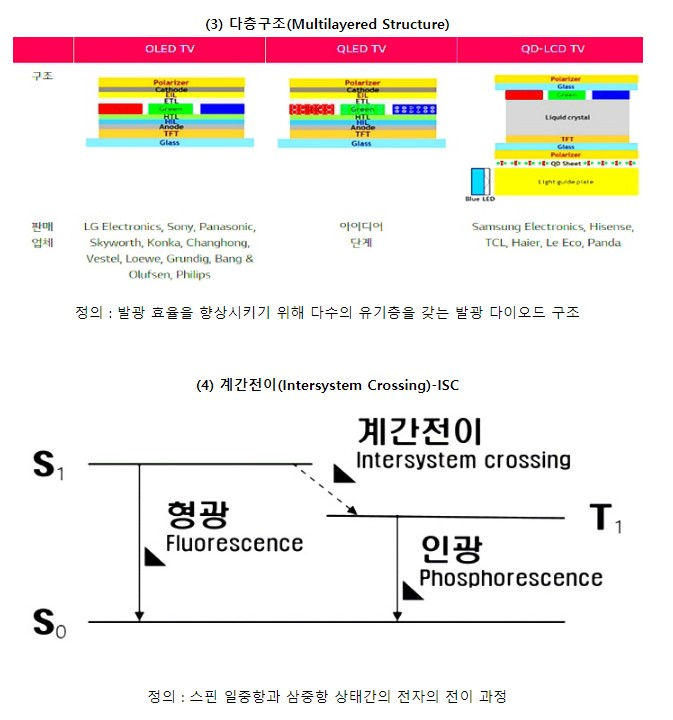
형광(Fluorescence)이란 OLED 디스플레이에서 사용하는 대표적인 발광(Luminescence) 방식 중 하나입니다. 발광이란 발광 물질 속의 전자가 높은 에너지 상태(들뜬 상태, excited)에서 낮은 에너지 상태(바닥 상태, ground)로 변화할 때, 감소한 에너지가 빛의 형태로 방출되는 현상입니다.
위 그림과 같이 전자가 바깥쪽 궤도에서 안쪽으로 이동할 경우에는 자체 보유 에너지가 줄어들면서 물질이 안정화 되며, 이때 남는 에너지는 빛과 같은 형태로 방출됩니다. 반대로 전자가 외부의 에너지를 흡수해 들뜨게 되면 바깥쪽 궤도로 상승하게 되는 원리입니다.
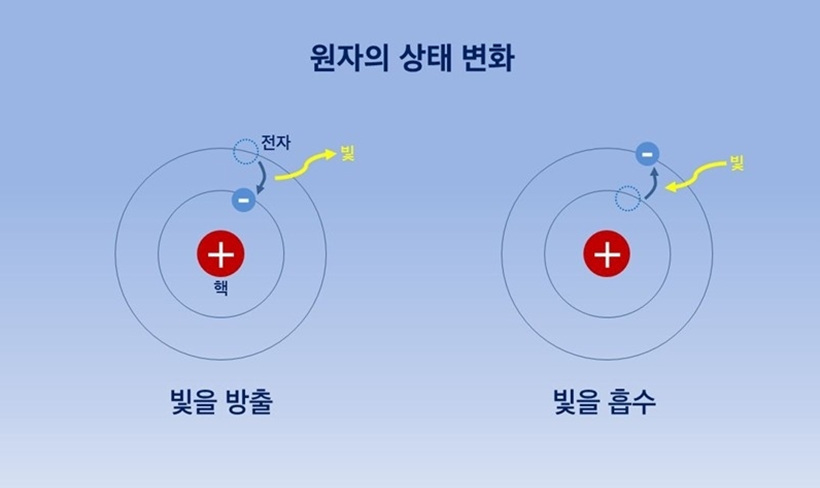
형광이란 바닥 상태의 발광 물질에 에너지를 주입해 해당 물질의 전자를 ‘들뜬 상태’로 만든 후, 짧은 시간에 다시 전자가 안정적인 ‘바닥 상태’로 변할 때 방출되는 빛을 디스플레이의 발광원으로 활용하는 방식으로, 위 그림과 같이 S1에서 S0으로 에너지 준위가 낮아지는 만큼의 에너지량이 빛의 형태로 방출됩니다. 하지만 형광 방식은 발광 에너지의 25%인 단일항 여기자(singlet exciton)만 활용되고, 75%를 차지하는 삼중항 여기자(triplet exciton)는 활용하지 못해 내부 양자효율이 25% 수준에 머물기 때문에 보다 효율적인 발광을 위해 인광 방식이 개발되었습니다.
인광(Phosphorescence)이란 형광(Fluorescence)과 더불어 OLED 디스플레이에서 사용하는 대표적인 발광(Luminescence) 방식 중 하나입니다. 발광이란 발광 물질 속의 전자가 높은 에너지 상태(들뜬 상태, excited)에서 낮은 에너지 상태(바닥 상태, ground)로 변화할 때, 감소한 에너지가 빛의 형태로 방출되는 현상입니다. 인광을 알기 위해서는 먼저 형광 발광 방식에 대한 이해가 필요합니다.

인광 방식은 형광 방식에서 열·진동으로 버려지는 나머지 75%의 에너지를 활용하는 원리입니다. 이리듐(Ir) 및 백금(Pt) 착화합물과 같이 무겁고 큰 금속을 포함한 발광체는 일반 유기물에 비해 전자가 존재할 수 있는 영역인 오비탈(전자의 확률 분포 공간)의 크기가 매우 커지게 됩니다. 이에 전자가 중심원소로부터의 영향을 적게 받게 되고, 일반 형광 발광체에서는 빛으로 나오지 못하던 삼중항 여기자(triplet exciton)와 단일항 여기자(singlet exciton)의 구분이 희미해지게 됩니다. 이에, S1의 들뜬 상태에서 형광으로 발생되어야 할 에너지를 T1이라는 상태로 이동시킬 수 있게 돼(계간전이) 삼중항 여기자까지 발광에 활용할 수 있게 됩니다.
인광 방식은 이론적으로 최대 100%의 내부 발광 효율을 만들 수 있는 장점이 있어 녹색과 적색 OLED용으로 상용화되었으나, 청색 재료의 경우 발광 파장대가 주요 삼원색인 R, G, B 중 가장 짧아 발광 에너지가 가장 큰 부분을 담당해야 하기 때문에 더 높은 안정성이 요구돼 구동 수명 개선 연구가 진행되고 있습니다.





PCB vs. FPCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board)
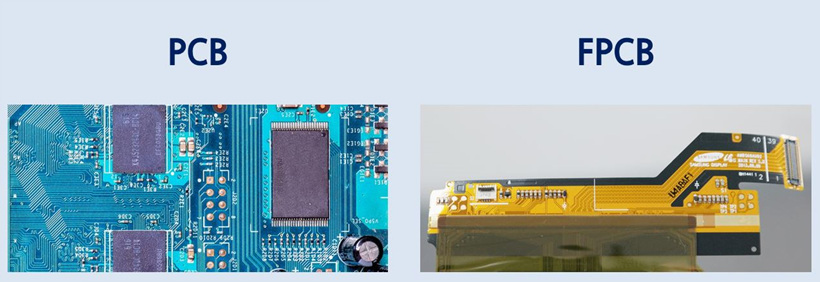
● PCB(Printed Circuit Board) : 인쇄회로기판, 전기적 신호를 전달하는 회로 부품
●FPCB(Flexible PCB) : 연성회로기판
PMD(개인용 모바일 기기)는 휴대성을 위해 크기가 작아야 함. 그래서 디스플레이를 뒤로 접어서 넣어야 해서 FPCB 사용함. 그리고 PMD 시장의 확장으로 사용 증대 중.
전자기기의 AP 가 명령하는 신호를 DDI(디스플레이 드라이버 IC)로 보내는 전달자 역할.
● FPCB의 장점
1. 얇고 유연해서 공간 절약. 제품 소형화 가능
2. 가벼워서 무게 절감
3. 높은 온도 견디고, 열 발산 잘함. 200~ 400도의 온도에서 견딜 수 있음
----------------------------------
OLED Display 관련 용어
Fundamental Terms
1. 흡수율(absorbance (absorptance, ABS))
The ratio of the total absorbed radiant or luminous flux to the incident flux. Standard unit of absorbance is percent (%) or a factor between 0 an 1.
2. 흡수계수(absorption coefficient)
The fraction of light of a given wavelength absorbed per unit distance in a medium; Standard unit of the absorption coefficient is fraction per meter (/m) [m^-1].
3. 어닐링(annealing)
heat treatment to the sample, in order to modify properties of materials/structures.
4. 양극(anode)
The electrode in which the holes enter into the organic layer when biased with positive voltage.
5. 주사슬(backbone)
The main structure of a polymer onto which substituents are attached.
6. 밝기 (Brightness)
the visual and subjective quality of how bright an object appears, or how much visible light is coming off the object being perceived by the eye. (47C/262/CD 61988-1/Ed1-2CD)
7. 칸델라(candela (cd))
The SI unit of luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 x 10^12 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian
8. 캐리어생성(carrier generation)
the process of creating electron-hole pairs.
9. 캐리어주입(carrier injection)
The process that the electrons and the holes enter into the organic semiconducting materials when an external electrical bias is applied.
10. 음극(cathode)
The negative electrode of an organic light-emitting device.
11. 발색단(chromophore)
A segment of an organic material that selectively absorb or emit certain wavelengths in the visible spectrum.
12. 색재현범위(color range)
the complete range of color of a display can generates. also called, color gamut
13. 색변이(color shift)
shift of CIE chromaticity coordinates due to degradation of the OLED
14. 농도소강(concentration quenching)
decrease of light-emitting efficiency as the concentration of dopant molecules
도펀트 분자의 농도에 따른 발광 효율 저하
dopant : 반도체에서 원하는 전기적 특성을 생성하는 데 사용되는 물질.
15. 전도대(conduction band)
the upper energy band in semiconductor that is not completely filled with electrons; electrons can conduct in the conduction band.
16. 접촉각(contact angle)
The angle between a solid and the tangent to a liquid surface at the contact point; useful in determining the wetting behavior of a liquid on a solid surface.
17. 열화(degradation)
a process describes that the operation characteristics of a device such as brightness, operating voltage, color coordinates, etc. changes undesirably in time.
18. 박리(delamination)
peeling off of a thin layer; peel off
19. 텍스터에너지전달(Dexter energy transfer)
a short-range energy transfer process where excitons diffuse from donor (D) to acceptor (A) sites via intermolecular electron exchange.
20. 도핑(doping)
In OLED, inroducing dyes into host organic materials to enhance the luminous efficiency, device stability, or change the light-emitting color
21. 전계발광(electroluminescence (EL))
the generation of light by electrical excitation. electroluminescence requires injection of electrons from one electrode and holes from the other, the capture of oppositely charged carriers (recombination), and the radiative decay of the excited electron-hole state (exciton) produced by this recombination process.
22. 전자친화도(electron affinity (EA))
the energy between the vacuum level and the bottom of the conduction band.
23. 전자저지층(electron blocking layer (EBL))
an organic layer with smaller electron affinity than the electron transporting layer that blocks the flow of electrons in an organic light-emitting device with multilayer structure.
24. 전자주입층(electron-injection layer (EIL))
a material that helps inject electrons from a cathode into an organic semiconductor layer in OLEDs
25. 전자수송층(electron-transporting layer (ETL))
a material that transports electrons from a cathode to the light-emitting layer (EML) where the radiative decay of the excited electron-hole state (exciton) occurs.
26. 전계인광(electrophosphorescence)
phosphorescence produced under an electrical excitation
27. 발광층(emissive layer (EML))
a light-emitting layer of OLEDs in which the radiative decay of the excited electron-hole state (exciton) occurs.
28. 밴드갭(energy band gap (Eg))
energy gap separating the valence band minimum and the conduction band maximum in semiconductors and insulators; unit eV.
29. 엑시머(excimer)
excited dimer which are bound in excited states only.
30. 엑시플랙스(exciplex (excited state complex))
excited complex formed with different molecules which are bound in excited states only. Emission fluorescence from the exciplex has a longer emission band than that of monomer fluorescence.
31. 엑시톤(exciton)
neutral bound excited states (electron-hole pair) formed with Coulombic binding energy.
32. 엑시톤저지층(exciton blocking layer (XBL))
an organic layer with a wide energy bandgap that blocks exciton diffusion, usually incorporated in an organic electrophosphorescence device for confining triplet excitons in an light-emitting layer.
33. 외부양자효율(external quantum efficiency (QA))
the ratio of the number of photons emitted from the device divided by the number of electrons injected from the electrical source.
34. 페르미준위(Fermi level (EF))
energy level in solids at which the Fermi-Dirac distribution function is equal to 0.5.
35. 전계효과트랜지스터(field effect transistor (FET))
A class of transistors in which current flows from a source to a drain via a channel whose resistance can be controlled by applying a voltage to a gate.
36. 플랫밴드전압(flat-band voltage (VFB))
a voltage at which there is no electrical charge in the semiconductor and, therefore, no voltage drop across it; in band diagram the energy bands of the semiconductor are horizontal (flat).
37. 형광(fluorescence)
Radiative decay of singlet excitons
38. 포스터에너지전달(Forster energy transfer)
a long range (~40-100 ), nonradiative, dipole-dipole coupling of donor (D) and acceptor (A) molecules. Since it requires that the transitions from the ground to the excited states be allowed for both D and A species, this mechanism only transfers energy to the singlet state of the acceptor molecule.
39. 반치전폭(半値全幅)(full-width-half-maximum (FWHM))
the spectral width in wavelength at the half maximum of the peak value
40. 유리전이온도(glass transition temperature (Tg))
a temperature at which an amorphous material undergoes from rubbery (elastic) to glassy (brittle) state as the temperature decreases.
41. 호모(highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO))
the highest occupied molecular orbitals (π orbitals)
42. 정공저지층(hole blocking layer(HBL))
an organic layer with a large ionization potential that blocks the flow of holes in an organic light-emitting device with multilayer structure.
43. 정공주입층(hole-injection layer (HIL))
a material that helps inject holes from an anode into an organic semiconductor layer in OLEDs
44. 정공수송층(hole-transporting layer (HTL))
a material that transports holes from an anode to the light-emitting layer (EML) where the radiative decay of the excited electron-hole state (exciton) occurs.
45. 호핑(hopping)
current conduction mechanism in which charge carriers are ''hopping'' from localized states to localized states assisted by the thermal excitation.
46. 내부양자효율(internal quantum efficiency (QA))
the ratio of the number of photons produced within the device to the number of electrons flowing through the device
47. 계간전이(intersystem crossing (ISC))
a process that electrons cross between the spin singlet and triplet states.
48. 이온화준위(ionization potential (IP))
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from a specified atom or molecule to such a distance that there is no electrostatic interaction between ion and electron. symbol IP, unit eV.
49. 수명(lifetime (t1/2))
lifetime that the device keeps the required performance; usually, it means a half lifetime - the time for the luminance decreases to half the initial value.
50. 루모(lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO))
the lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (π* orbitals)
51. 휘도(luminance (L))
The luminous intensity of a surface in a given direction per unit of orthogonally projected area of that surface. It is measured in candela per square meter. cd/m2
52. 발광(luminescence)
The emission of light by a substance for any reason other than a rise in its temperature. In general, atoms of substances emit photons of electromagnetic energy when they return to the ground state after having been in an excited state. If the exciting cause is a photon, the process is called photoluminescence; if it is an electron it is called electroluminescence
53. 발광효율(luminous efficiency (hL))
The ratio of the total power of light emitted, taking into account of the sensitivity of the human eye, to the electrical input power. symbol hL, unit lm/W
54. 광속(luminous flux)
The rate of flow of light energy, taking into account the sensitivity of the observer or detector to the different wavelengths, i.e., photometrically weighted radiant flux density; unit lumen [lm] = cd·sr
55. 이동도(mobility)
proportionality factor between electron drift velocity and electric field as well as carrier concentration and conductivity of semiconductor; symbol m, unit cm^2/Vs
56. 비발광재결합(non-radiative recombination)
type of recombination where energy is released in the form other than electromagnetic radiation.
57. 유기EL (organic light-emitting diode (OLED))
an organic semiconductor device that emits light under the electrical excitation
58. 유기반도체(organic semiconductor)
a new class of semiconductor materials based entirely on organic components
59. 인광(phosphorescence)
The emission of light from an excited molecule of spin triplet state after it has been exposed to and excited by some form of radiation.
60. 픽셀(pixel (PXL))
smallest element that is capable of generating full functionality of a display; an active picture element, when combined together in a matrix, forms a character, symbol, or graphics; In general R, G, B subpixels (or dots) consist a pixel.
61. 해상도(resolution)
capability of displaying images in detail; in general defined as dot per inch (dpi) or pixel per inch (ppi).
62. 세그먼트(segment)
An active element of a digit
63. 스펙트럼변화(spectrum change)
change of the specral shape of a R, G, B subpixel compared with its initial spectrum.
64. 명암점 성장(white/dark spot growth)
growth of a white spot or dark spot under operation in time.
65. 부화소(sub-pixel)
the smallest element of a display that can be addressed, typically a primary color element; see dot. (3. 201 in 47C/262/CD 61988-1/Ed1-2CD)
66. 박막트랜지스터(thin film transistor (TFT))
a transistor formed on the surface of a substrate as a thin film
67. 문턱전압(threshold voltage (Vth))
A voltage applied to the gate in a thin film transistor above which current can to flow through its main conduction path.
68. 턴온전압(turnon Voltage (Von))
A minimum voltage that the light emission from the pixel is above the eye detectability
공정/구조
1. 스트리퍼(stripper)
감광액을 벗겨내는 약품
2. 프리베이크(pre-bake)
PR 코팅후 용매를 제거하기위해 열을 가하는 공정
3. 포스트베이크(post-bake)
PR 현상후 PR을 경화시키기 위하여 열을 가하는 공정
4. pst exposure bake
격벽 형성시 nagative PR을 사용할 경우, UV 노광 후 PR을 경화시키는 공정
5. 세정
세정공정 기판표면의 오염물질을 제거하는 공정; 리소그래피를 처음으로 하는 각 공정사이에서 반드시 행해야 하는 것으로 표면 청정화를 위한 공정
6. 스트라이프형(stripe-type 소자)
긴 막대모양으로 RGB 부화소가 나란히 배열된 형태
7. 델타형(delta-type 소자)
삼각형 모양으로 RGB 부화소가 배열된 형태
8. 에이징(aging)
소자를 초기열화시켜 안정화시키는 과정
9. 양극배선(anode stripe)
수동형 소자에 사용되는 긴 막대모양의 양극 배선
10. 음극배선(cathode stripe)음극 배선
11. 격벽(cathode separator)
유기물 위에 증착되는 상부전극을 stripe형태로 분리하기 위해 필요한 구조물로 하부전극 stripe과 직 교 되도록 형성함. The respective cathodes to be completely separated from the adjacent cathodes and thereby prevents shorts between the pixels a structure, formed with a lift-off negative photoresist in an inverse taper shape (a width of 5 to 10μm and the thickness of approximately 1μm), that causes the respective cathodes to be completely separated from the adjacent cathodes and thereby prevents shorts between the pixels.
12. 쉐도우 마스크(Shadow mask)
유기물이나 상부전극 등을 소자의 일부분에 증착시키기 위해 필요한 mask; device allowing selective deposition of organic materials on the substrate by blocking molecular beam in selected areas; In a full color display, the three primary colors- red, green and blue- are evaporated through a SUS shadow mask to prevent the regions that are not subject to vapor deposition.
13. 오픈 마스크(open mask)

오픈마스크(Open Mask, OM)는 OLED 디스플레이 제조 시 특정 위치에만 증착이 되도록 하는 얇은 판을 의미합니다. 디스플레이 제조 과정에서 백플레인 (Backplane)이 완료된 후 그 위에 발광층을 형성하기 위한 증착공정에서 사용됩니다.
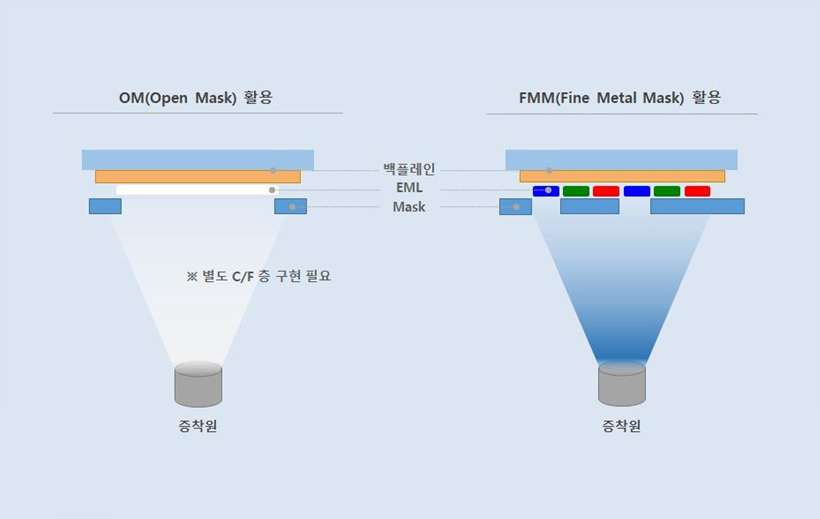
증착공정에서 활용하는 마스크에는 OM과 FMM(Fine Metal Mask)이 있으며 OM은 디스플레이 전면을 증착하기 위해 디스플레이가 작동하는 범위 내에 가림 부위가 없는 개방(Open)된 마스크입니다. 발광층을 한 가지 색깔의 발광물질로 증착하거나 EIL, HTL 등의 층을 증착할 때에도 활용합니다.
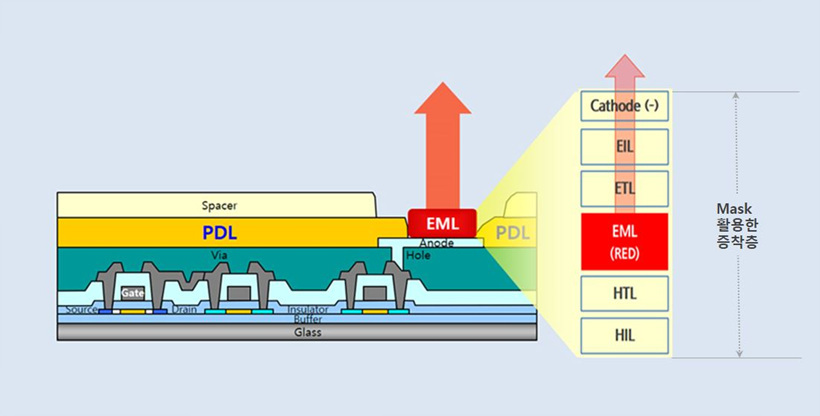
반면, FMM은 구현하는 발광층의 Sub-pixel에 색깔을 달리하기 위해 사용하며 초미세 홀(Hole)을 가지고 있습니다. 여러 단계의 증착과정을 진행해야 하므로 정확한 정렬이 필요하여 OM만을 활용하는 기술보다 난도가 높다고 할 수 있습니다.
OLED 디스플레이 발광층을 OM을 활용하여 증착된 경우 한 색깔만을 낼 수 있게 되므로 색구현을 위해 컬러필터(Color Filter, C/F)와 같은 별도의 층을 두어야 합니다. 이와 다르게 FMM을 활용하여 RGB 발광층이 만들어진 경우에는 C/F가 필요하지 않습니다. 즉, Sub-pixel에 FMM을 활용하는 기술이 난도가 높긴 하지만 OM을 활용한 방식 대비 빛을 차단하는 필터가 없어지므로 빛 효율이 좋다고 할 수 있습니다.
OM 소재로는 금속을 활용합니다. 증착공정은 고온 환경에서 진행되어 온도변화에 따른 열팽창이 발생하며 화소 사이에 정렬이 틀어질 수 있습니다. 이러한 이유로 열팽창을 최소화할 수 있는 특수 금속이 적극 활용됩니다.
마스크를 제조하는 대표적인 방법으로는 금속판을 포토/에칭 기술을 활용하는 법, 레이져 가공법 및 기계적인 절삭법이 있습니다.
14. 알지비 마스크(RGB mask)
15. 스페이서(spacer)
전극과 봉지용 can 사이의 간격을 유지하도록 넣어주는 물질
16. 스테퍼(Stepper)
정렬 노광기의 일종으로 WF 1매에 몇 개의 ?Chip 단위로 전후 좌우로?이동하면서 각 단위 Chip마다 정렬 및 노광을 실시하는 ?장비. 따라서??WF 1매를 한 번에 정렬 노광하는 장비 보다 정교한 현상화 가 가능하다
17. 얼라인 키(Align key)
정렬 할 때 필요한 마크
18. 기판전처리
다음 공정 전의 기판 표면 처리 공정
19. 두께균일도
증착된 박막 두께의 균일도
20. 진공 열증착(vacuum thermal evaporation)
진공에서 저항 가열 방식으로 물질을 기화시켜 기판에 박막을 형성하는 방법; common technique used to deposit thin film materials; material to be deposited is heated in vacuum, 10-6 Torr - 10-7 Torr range, until it starts evaporating; vapor of material is condensing on the cooler substrate exposed to the vapor.
21. 플라즈마
표면처리 플라즈마에 의해 생성된 라디칼을 이용하여 기판 표면을 개질하는 방법
22. 투명전극(transparent electrode)
A layer or an electrode which has both electric conductivity and transmittance of visible light. A typical material is ITO(indium tin oxide)
23. 딥코팅(Dip-coating)
a process that coating is obtained by immersing the substrate in the plastic solution
24. 개구율(Aperture ratio)
a ratio of the pixel area available for light modulation to the geometrical pixel area
25. 모듈(Module)
An assembly that comprises the cell plus display drivers that control light and deliver host computer data to the cell, as well as a backlight assembly consisting of fluorescent lamps, light pipes, and associated diffusers and reflectors, all contained within a rigid sheet-metal structure
26. 원형편광판(circular polarizer)
An optical part that transmits only specific polarized light
27. 크로스토크(Cross-talk)
an undesirable luminance variation on the part of a display area produced by an image display on the another part of the display
28. 이방성 전도 필름(ACF,anisotropic conductive film)
29. 스퍼터링(sputtering)
bombardment of solid target by high energy chemically inert ions extracted from plasma causes ejection of atoms from the target which are then redeposited on the surface of the substrate purposely located in the vicinity of the target
30. 열증착(evaporation)
common technique used to deposit thin film materials; material to be deposited is heated in vacuum until it melts and starts evaporating' vapor of material is condensing on the cooler substrate exposed to the vapor; common technique in thin film metal deposition
31. 디스펜싱(dispensing)
distribution of sealant
32. 도판트(Dopant)
element introduced into semiconductor to estiblish either p-type or n-type conductivity in a conventional semiconductor. Dyes are doped into host organic materials
33. 캐니스러(canister(seal-cap)
encapsulation을 위해 덮어주는 덮개
34. 건식 식각(dry etching)
etching process in the gas-phase
35. 습식 식각(wet etching)
etching process is relying on chemical reaction in the liquid phase.
36. 백색균일도(white uniformity)
Full White Pattern을 인가하였을때 얼마나 고르게 백색을 구현하는가를 나타내는 정도
37. 노광(exposure)
irradiation of resist with radiaton of adequate wavelength; 노광, 감광액을 도포한 표면에 우너하는 패턴을 가진 Mask를 정렬시켜 자외선 등을 쬐는 작업. 이후 현상작업에 의해 Mask의 pattern이 형 성됨
38. 보조전극(auxiliary electrode)
ITO의 저항을 줄이기 위하여 ITO위나 아래에 깔아 사용하는 전극으로 저항이 낮은 금속을 사용.
39. 거칠기(roughness)
lack of planarity of solid surface at the atomic level; surface roughness is measured as a difference between highest and deepest surface features
40. 현상액(developer)
liquid used to dissolve selected parts of the resist following exposure
41. 포토마스크(photomask)
mask used in photolithography to block resist exposure in selected areas; consists of chrome opaque areas supported by very high quality quartz plate transparent to UV radiation
42. 정열(Alignment)
mask를 특정 부분에 위치시키는 것. Positioning of the mask in lithographic process
43. 이빔 증착(e-beam evaporation)
material is evaporated as a result of highly localized heating by bombardment with high energy electrons generated in an electron gun and directed toward the surface of source material confined in the crucible.
44. 포토리소그라피(photolithography)
pattern definition method which uses UV radiation to expose the resist; the most common lithography technique in semiconductor manufacturing
45. 현상(development)
photolithography 공정에서 감광액 도포 및 노광후 필요한 Pattern만을 남기고 불필요한 부분의 감광 액을 제거하는 작업.
46. 감광액(photoresist)
PR ; 감광성 수지를 말하며 구성 성분은 Polymer, Solvent, Sensitizer로 대표되며 현상되는 형태에 따라 양성(Positive)과 음성(Negative)으로 나뉨.
47. 베이크(bake)
photoresist를 도포한 후 열에 굽는 것
48. 기판(Substrate)
Plate, generally transparent, made of e.g. glass or plastic sheet, covered with several layers(electrode, sealing and surface alignment layers), forming the mechanical structure of a liquid crystal cell.
49. 흡습제 방(housing-getter)
position of getter
50. 피시비(PCB)
printed circuit board, 인쇄 배선판. 위에 저항, 콘덴서, 코일, TR, IC, LSI, 스위치 등의 부품을 장치 하고 납땜하여 회로기능을 완성시킨 것.
51. 페키징(packaging)
process of enclosing the semiconductor chip or discreet device in the package
52. 스트리핑(stripping)
process of material emoval from the substrate surface; typically implies that removal is not carried out for the patterning purpose
53. 타겟(target)
sputtering에 의해 증착할 때 사용되는 금속 원재료 54. 티에이비(TAB) tape automated bonding, one-step process used to connect chip to the package; package leads are formed on the flexible tape
55. 티씨피(TCP)
Tape Carrier Package 56. 도핑(Doping) the introduction dopant into host during the manufacturing process for the purpose altering the physical properties of individual layer
57. 흡습제(getter)
the materials that removes moisture from the device 58. 보호층(passivation) thin barrier coating for preventing absorption of the moisture and oxygen 59. 얼라이너(aligner) tool allowing positioning of the mask in lithographic process relative to a substrate prior to exposureof the resist 60. 증착(Deposition) transfer the material from the source to the substrate by physical means without changing its chemical composition
61. 봉지(encapsulation)
used to prevent the exposure of the thin film organics to moisture and oxygen by bonding a sheet metal canister containing an alkaline eath oxide desiccant to the substrate glass
알칼리 eth 산화물 건조제를 포함하는 판금 캐니스터를 기판 유리에 결합하여 박막 유기물이 습기와 산소에 노출되는 것을 방지하는 데 사용됩니다.
62. 자외선 세정(uv cleaning)
UV 자외선을 이용하여 생성된 오존을 통해 ITO 표면을 산화하는 방법
63. 버퍼 챔버(buffer chamber)
64. 하부 전극간 절연층(inter insulation layer)
65. 씨디(C.D (Critical Dimension))
공정 중에 나타나는 Device의 평면적인 치수를 의미하며 일반적으로는 선폭이라고도 함.
AM 구동 관련 용어 정의 - 삼성 SDI
1. 면적비계조(area ratio gray control)
발광 면적 비를 이용한 gray control방법
2. 정전압구동(Constant voltage driving)
EL diode의 정전압 구동
3. 전류구동(current driving)
전류에 의한 구동
4. 전류프로그래밍(current programming)
video 신호를 전류값으로 입력하여 구동하는 방법
5. 디에이컨버터(DAC(Digital to Analog Converter))
digital 신호를 analog 신호로 변환하는 장치
6. 델타화소구동(delta type)
R, G, B의 sub-pixel의 배치를 delta 방식(삼각형모양)으로 배치하여 구동하는 방법
7. 구동티에프티(driving tft)
pixel circuit에서 EL diode에 흐르는 전류를 흐르게 하며, 전류를 조절하여 밝기를 조절해주는 tft
8. 전류이동도(field effect mobility)
tft에서 gate 전압 변화에 의한 drain, source간의 전류 유동도
9. 전압강하(IR drop)
EL 구동을 위한 전류와 배선 저항에 의해 생기는 전압강하
10. 로딩효과(loading effect)
display에 띄우는 화면에 따라 흐르는 전류가 달라지고, 이에 따라 IR drop 이 달라져서 나타나는 현상
11. 저온폴리실리콘(LTPS (low temperature poly silicon))
저온에서 제조된 poly-crystalline silicon
12. 엘유티
13. LUT(look-up table)
14. 화소구동회로(pixel driving circuit)
circuit for driving EL diode of each sub-pixel
15. 알씨딜레이(RC delay)
display 내의 resistor, capacitor 성분에 의한 signal의 delay.
16. 포화영역(saturation mode)
tft의 구동조건에 있어서 saturation 동작 영역
17. 스위칭티에프티(switching tft)
scan driver의 선택신호 시 data driver의 data를 pixel에 전달하는 tft
18. 문턱전압자동보정(Threshold voltage auto calibration)
19. 문턱전압보상(Threshold voltage compensation)
uniform한 display를 위하여 display 전역에서 threshold voltage 차이를 보상하는 것.
20. 시분할계조(time ratio gray control)
시간을 배분하여 전류를 단속하여 흘려줌으로써 행하는 gray 구현법
21. 전압프로그래밍(voltage programming)
display 구동을 위하여 data 신호를 voltage로 입력하는 방법
22. 선형영역
COG, COF, COP는 이런 DDI를 디스플레이 또는 인쇄회로 기판에 연결하는 형태나 방식을 말하는 용어입니다. 디스플레이 패널에 사용되는 기판에 드라이버 IC를 부착할 때는, 기판의 종류나 부착 방법에 따라 다른 기술이 적용됩니다.
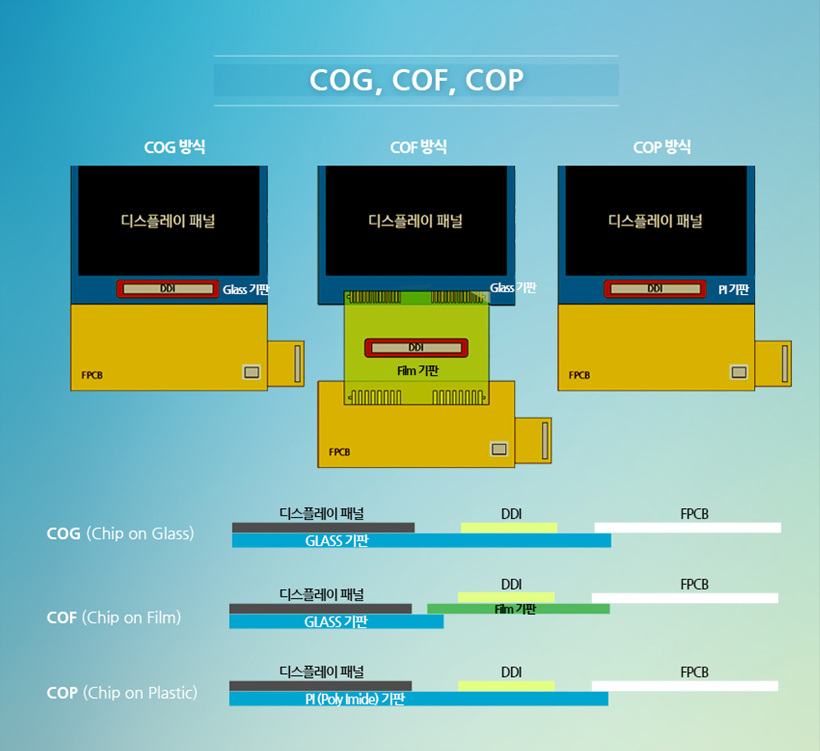
COG (Chip On Glass)는 디스플레이 유리 기판 위에 직접 드라이버 IC를 탑재하는 방식입니다.
COF (Chip On Film)는 드라이버 IC가 실장 된 박막인쇄회로가 형성된 필름을 말하는 것으로, 이 필름을 디스플레이 기판과 FPCB에 연결합니다. 얇은 필름 타입 위에 부착하기 때문에 필름을 말거나 접을 수 있어, 패널이 탑재되는 제품의 두께나 크기를 줄이는 유연한 설계가 가능합니다.
COP (Chip On Plastic)는 디스플레이 기판으로 사용되는 유연한 PI(폴리이미드)에 드라이버 IC를 직접 부착하는 방식입니다.
COF와 COP는 유연한 소재의 필름과 폴리이미드 기판에 DDI를 부착하는 만큼 플렉시블 디스플레이나 풀 스크린 등에 주로 활용하는 방식입니다. 유연한 소재에 적용하기 때문에 제품의 상하단 베젤을 줄이는 등 공간 활용성이 우수합니다.
PM 구동 - 현대LCD
1. 이방성전도접착제(ACA (Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive))
이방성 도전볼 및 접착제를 함유한 액상으로 TCP IC, Bump IC, COF, FPC등을 Bonding 하기 위하 여 사용함.
2. 이방성전도필름(ACF (Anisotropic Conductive Film))
이방성 도전볼 및 접착제를 함유한 Film으로 TCP IC, Bump IC, COF, FPC등을 Bonding 하기 위하 여 사용함.
3. 능동구동(Active matrix )
구동하고자 하는 Dot에 Frame 내내 On Sgnal이 입력되게 구동하는 방법으로 Data 기억 소자를 가 짐.
4. 어드레싱(Addressing)
특정한 프로세스나 네트워크 장치와 같은 고유한 영역을 식별하는데 사용되는 데이터 구조
5. 브릿지(Bridge)
Lead와 Lead 사이에 Solder가 연결되어 Short 되어있는 형태.
6. 범프칩(Bump Chip)
Chip상의 Al Pad위에 Gold를 Bumpping한 IC.
7. 칩(Chip)
SMD Type의 저항이나 커패시터등을 총칭.
8. 씨오비(COB (Chip On Board))
PCB나 FPC등 Board에 Al이나 Au Wire를 Bonding하여 실장한 Type의 제품. The display driver is constructed on the PCB with the electrical connections made by Al or Au wires and then the entire area is covered with epoxy.
9. 씨오에프(COF (Chip On FPC))
얇은 Polyimide Film위에 ACF(or ACA) Bonding이나 열합금 방법으로 Bump IC를 실장한 Type의 제품.
10. 씨오지(COG (Chip On Glass))
Panel의 ITO(Indium Tin Oxide) 단자에 Bump IC를 ACF나 ACA를 이용하여 실장한 Type의 제품; the display driver is mounted on the surface of the glass and then covered with epoxy.
11. 콤(COM(Common,Row))
Duty Ratio(1/n) 에 따라 1번의 Select 전압과 N-1번의 Non Select 전압을 유지하는 Scan 파형을 가지며 Cathode와 연결됨.
12. 정전류(Constant Currnet)
전류 구동 방법으로 일정한 전류를 각 Pixel에 흘려 주는 상태
13. 콘트롤러(Controller)
Scan Driver 회로와 Data Driver에 동기 클럭을 공급하며, 영상 Data의 흐름을 결정하여 주는 기능 을 담당하는 IC.
14. 전류구동드라이버(Current Driver)
일정한 전류의 In, Output을 Control 할수 있는 Driver로 OLED의 구동에 사용.
15. 데이터드라이버(Data Driver)
영상신호를 출력하는 Driver로, Seg Driver, Column Driver라고도 불리우며, Anode에 연결됨.
16. 데이터라인(Data Line)
매트릭스 배열에 입력되는 신호가 들어가는 Anode라인.
17. 직류승압회로(DC/DC Converter)
입력으로 들어온 직류전압 Source를 이용하여 Operating에 필요한 Driving Voltage를 생성하여 주는 승압 회로임.
18. 듀티비(Duty ratio)
Cathode Line에 인가되는 선택 시간과 선택 파형이 모든 전극을 1회 주사하는데 걸리는 시간. 즉 주 기와의 비를 의미함.
19. 플리커(Flicker)
같은 상태의 화면이 밝기가 일정하지 않고 시간에 따라서 변화는 현상.
20. 에프피씨(FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit))
Base film (Polymide)과 Cover film(Polymide) 사이에 동박을 이용하여 Pattern을 형상시킨 Connector.
21. 프레임(Frame)
순차 주사구동에 따라서 구성되는 1개 화면을 표시하는 시간.
22. 프레임주파수(Frame frequency)
순차 주사구동에서 방식에서 선택 파형이 다시 반복될때까지의 시간의 비. Number of Frames displayed per second
23. 아이엘비(ILB (Inner Lead Bonding) TCP나 COF등의 제작시 Chip과 기판 전극과의 Bonding을 의미.
24. 잔상(Image Sticking, Residual Image, Baking Image)
동일화면을 장시간 켜 두었을 때 화면이 바뀌어도 상이 남아 있어 오랜동안 없어지지 않고 남아 있 는 것.
25. 누설전류(Leak Current)
Anode와 Cathode 사이에 역전압을 인가했을 때 흐르는 전류.
26. 라인어드레싱(Line addressing)
화소수가 많은 것은 주사선을 차례로 선택하여 주사선에 연결된 모든 화소에 동시에 신호전압을 걸 어주는 방법.
27. 다중구동(Multiplex Drive)
Dot Matrix나 여러 개의 Icon들을 동시에 독립적으로 각각의 화소나 Icon을구동하는 방식으로 독립 적인 N개의 전극이 존재하면 선택 파형은 N에 동시에 인가하지 않고 N개의 전극에 각각 한번씩 인가 하여 구동하는 방식.
28. 오엘비(OLB (Outer Lead Bonding))
TCP나 COF의 Outer Lead와 Glsss기판의 전극을 이방성 도전필름(ACF)을 이용 Bonding하는 것.
29. 피에이엠(PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation))
영상 Data의 음영 즉, Gray를 구현하는 방법중의 하나로 펄스의 높이를 변조하는 방식.
30. 수동구동(Passive matrix)
구동하고저 하는 Dot에 On Sgnal을 한프레임에 1/N(N=Duty) 시간만큼 공급하는 방법으로 구동 방 법이 간단함.
31. 피씨비(PCB (Printed Circuit Board))
유리섬유등의 원판위에 동판을 이용하여 회로를 집적한 Board로 부품 실장 및 Connection을 위함.
32. 선충전(Pre-Charge)
구동시 Panel의 Saturation(Vth) 이하의 전류을 미리 흘려 준뒤에 Operting 전류를 흘려 주는 구동 방법.
33. 피더블유엠(PWM (Pulse Width Modulation))
영상 Data의 음영 즉, Gray를 구현하는 방법중의 하나로 펄스의 폭을 변조하는 방식.
34. 큐에프피(QFP (Quarter Flat Package))
PCB나 FPC에 SMT(Surface Mount Technology)를 위한 IC Package로 Package의 4방향으로 Lead 가 나와 있는 형상을 말한다.
35. 스캔드라이버(Scan Driver)
Line Selection 신호를 출력하는 IC로 Row Driver 또는 Com Driver라고도 부리우며 순차적으로 라 인을 활성화시켜 화면을 표시하는 회로.
36. 표면실장(SMD (Surface Mount Device)
PCB, FPC등에 IC, CHIP 부품 등을 표면 실장하는 공정.
37. 표면실장기술(SMT (Surface Mount Technology))
PCB, FPC등에 IC, CHIP 부품 등을 표면 실장하는 기술.
38. 탭(TAB (Tape Automated Bonding))
Interconnection의 일종으로 Panel과 TCP IC를 Bonding하는 방식을 일컬음. driver or controller electronics are encapsulated in a thin, hard bubble package, of which the drive leads extend from the bubble package on a thin plastic substrate.
39. 티씨피(TCP (Tape Carried Package))
Poly Imide Flim위에 Gold Bump로 단자 처리된 IC를 실장 시킨 Type
40. 턴온전압(Turn-On Voltage)
Panel에 전압을 인가 했을시 Pixel의 On상태가 눈으로 감지할수 있을때의 전압.
41. 방전(Discharging)
Constrast Ratio가 일정 정도 이상을 유지하는 좌우, 상하의 시야각.
42. 역바이어스(Reverse Bias)
고분자 재료 <발광재료>
1. PPP [B]
poly(paraphenylene)
2. m-LPPP
methyl substituted ladder-type poly(paraphenylene)
3. MEH-PPV [R]
poly[2-methoxy, 5-('-ehtyl-hexyloxy)-1,4-phenylene vinylene]
4. PVK [B]
poly(N-vinylcarbazole)
5. PDHPT
poly(2,5-diheptyl-1,4-phenylene-alt-2,5-thienylene)
6. PBPS [B]
poly[bis(p-n-butylphenyl)silane]
7. PPV [G]
poly (p-phenylene vinylene)
8. PF [B] polyfluorene
9. PFV [B]
10. Al-PPV [Yellow]
11. CN-PPVs [orange]
<정공 주입 ․ 수송 재료>
1. PEDT
polyethylene dioxythiophene
2. PSS
polystyrene sulphonate
3. PEDOT/PSS
poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonic acid)
4. PEtTPAEK
PTPDES
5. PMDA-DBABBD PI
poly[N,N'?diphenyl?N,N'?bis(4?aminobiphenyl)?(1,1'?biphenyl)?4,4'?diamine pyromellitimide]
6. PVK
7. TPD-PMA
8. TPD-PS
9. TPD-PV
10. PMMA
11. PVdF-HFP
12. PC
13. PMDA-ODA PI
14. PEI
단분자 재료
<전자주입재료>
1. LiF
lithium fluoride
2. Liq
(8-hydroxyquinolinolato)-lithium
3. CsF
cessium fluoride
4. NaF
sodium fluoride
<전자 수송 재료>
1. Alq3
tris(8-quinolinolato)aluminum (Ⅲ) [G]
2. BAlq
bis(2-methyl-8-quinolinolato)(p-phenylphenolato)aluminium(Ⅲ)
3. Bphen bathophenanthroline
4. BCP
2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenantroline
5. OXD7
1,3-bis(N,N-t-butyl-phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
6. TAZ
3-phenyl-4-(1'-naphthyl)-5-phenyl-1,2,4-triazole
7. 4MAlq3
SSOSS
8. spiro-PBD
spiro-2-biphenyl-4-yl-5-(4-t-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
9. TPBI
10. BMT-2T
5,5"-bis (dimesitylboryl)-2,2'-bithiophene
11. BMT-3T
5,5"-bis (dimesitylboryl)-2,2':5',2"-terthiophene
12. PyPYSPyPy
13. COT
14. PF-6P
15. PBD
2-biphenyl-4-yl-5-(4-t-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole 16. TPOB 1,3,5-tis[5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl] benzene
<정공 저지(억제) 재료>
1. BCP
2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenantroline
2. BAlq
bis(2-methyl-8-quinolinolato)(p-phenylphenolato)aluminium(Ⅲ)
3. PBD
2-biphenyl-4-yl-5-(4-t-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
4. TAZ
3-phenyl-4-(1'-naphthyl)-5-phenyl-1,2,4-triazole
5. niBr
N-2,6-dibromophenyl-1,8-naphthalimide
6. TPBi
2,2',2"-(1,3,5-benxenetriyl)tris-[1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazole]
7. Palq aluminium(Ⅲ)
bis(2-methyl-8-quinolinolato)4-phenolate
8. Salq aluminium(Ⅲ)
bis(2-methyl-8-quinolinolato)triphenylsilanolate
<발광 도판트 재료(R, G, B)>
1. Alq3 [G]
tris(8-quinolinolato)aluminum (Ⅲ)
2. PtOEP [R]
2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octaethyl-21H,23H-porphine platinum (2)
3. DCM [R]
4-(dicyanomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)-4H-pyran
4. DCM2 [R]
4-(dicyanomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(juloidin-4-yl-vinyl)-4H-pyran
5. DCJTB [R]
4-(dicyanomethylene)-2-t-butyl-6-(1,1,7,7-tetramethyljuloidyl-9-ehyl)-4H-pyran
6. Rubrene [R] 5,6,11,12-tetraphenylnaphthacene
7. Ir(ppy)3 [G]
fac tris(2-phenylpyridine) iridium
8. Btp2Ir(acac) [R]
bis(2-(2'-benzo[4,5-a]thienyl)pyridinato-N,C3') iridium(acetylactonate)
9. Firppy [B]
fac-tris[2-(4,5'-difluorophenyl)pyridine-C'2,N] iridium(Ⅲ)
10. Eu[DBM]3(phen) [R]
tris(1,3-diphenyl-1,3-propanediono)(monophenanthroline)Eu(Ⅲ)
11. TPP [R]
tetraphenylporphine
12. ZnTPP [R]
zinc-tetraphenylporphine, 아연-테트라페닐포르핀
13. TPC [R]
tetraphenyl chlorin, 테트라페닐 염소
14. (dppy)BF [B]
1,6-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)pytidine boron complex
15. LiPBO [B]
2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazolato lithium
16. AND [B]
9,10-di-(2-naphthyl) anthracene
17. TBP [B]
2,5,8,11-tetra-tbutylperylene
18. DCDDC [R]
3-(dicyanomethylene)-5,5-dimethyl-1-[(4-dimethylamino)styryl]cyclohexene
19. AAAP [R]
6-methyl-3-{3-(1,1,6,6-tetramethyl-10-oxo-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-1H,4H,10H-11-oxa-3a-azabenz o[de]anthracence-9-yl)acryloyl}pyran-2,4-dione
20. Bt2Ir(acac) [yellow]
bis(2-phenylbenzothiozolate-N,C2')iridium(acetylacetonate)
21. (ppy)2Ir(acac) [G]
bis(2-phenylpyridine)iridium (Ⅲ) acetylacetonate
22. C-545T [G]
10-(2-bezothianzolyl)-1,1,7,7-tetramethyl-2,3,6,7-tetradro-H,5H,11H-[1]benzo-pyrano[6,7,8-ij] quinolizin-11-one
23. DEQ [G]
N,N'-diethylquinacridone
24. 4MAlq3 [G]
25. DPVBi [B]
4,4'--bis(2,2'-diphenylvinyl)-1,1'-biphenyl
26. BFA-IT [B]
2,5-bis{4-[bis-(9,9-dimethyl-2-fluorenyl) amino]phenyl}thiophene
27. spiro-oligo (p-phenylene) [B]
spiro-oligo (p-phenylene)
28. TBSA [B]
9,10-bis[(2", 7"-t-butyl)-9',9"-spirobifluorenyl]anthracene
29. ter-fluorene [B]
terfluorene
30. ter-spirobifluorene [B]
ter-spirobifluorene
31. DSA [B]
32. DSA-Amine [B]
33. α-DNA [B]
34. β-DNA [B]
35. Ph3Si(PhTDAOXD) [B]
36. Zn(PhPy)2 [B]
37. Zn(BOX)2 [B]
38. BAlq3 [B]
39. DPP [R]
6,13-diphenylpentacene
40. (PPA)(PSA)Pe-1 [R]
3-(N-Phenyl-N-p-tolylamino)-9-(N-p-styrylphenyl-N-p-tolylamino)perylene
41. BSN [R]
1,1'-dicyano-substituted bis-stylnaphthalene
42. DDP [R]
43. Periflanthene [R]
Periflanthene 44. BTX [R] benzothioxanthene
45. Ir(mppy)3 [G]
46. Zn(Phq)2
47. Be(bq)2
48. Zn(BTZ)2
49. Zn(ODZ)2
50. Zn(TDZ)2
51. BE(5Fla)2
bis(5-hydroxyflavonato)beryllium
52. Zn(3Fla)2
bis(3-hydroxyflavonato)zinc
53. Zn(5Fla)2
bis(5-hydroxyflavonato)zinc
54. Zn(BIZ)2
55. Qd-1
56. Qd-2
57. Qd-3
58. C-540
59. Pyrazoline
60. tBu-PTC
61. Perylene
62. BCzVBi
63. Ir(BQ)3
64. Ir(ThPy)3
65. Ir(BO)3
66. Ir(BT)3
67. Ir(BTPy)3
68. Ir(BQ)2acac
69. Ir(ThPy)2acac
70. Ir(BO)2acac
71. Ir(BT)2acac
72. Ir(BTPy)2acac
73. Pt(thpy)2 [Y]
cis-bis[2(2-thienyl)pytidine-N,C3]platinum(Ⅱ)
74. PtOX [R]
platinum(Ⅱ) 2,8,12,17-tetraethyl-3,7,13,18-tetrametyl porphyrin
75. Eu(TTA)3phen [R]
TTA = thenoyltrifluoroacetone, phen = 1,10-phenantrroline
76. thp2Ir(acac) [G]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(2-(2'-thienyl)pyridinato-N,C3')(acetyl acetonate)
77. dpo2Ir(acac) [G]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(2,4-diphenyloxazolato-1,3-N,C2')(acetyl acetonate)
78. C6Ir(acac) [G]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(3-(2-benzothiazolyl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-1-benzopyran-2-onato-N',C4)(acetyl acetonate)
79. bon2Ir(acac) [Y]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(2-(1-naphthyl)benzooxazolato-N,C2')(acetyl acetonate)
80. βbsn2Ir(acac) [Y]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(2-(2-naphthyl)benzothiaolato-N,C2')(acetyl acetonate)
81. op2Ir(acac) [G]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis(2-phenyl oxazolinato-N,C2')(acetyl acetonate)
82. Firpic [B]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis[4,6-di-fluorophenyl)-pyridinato-N,C2']picolinate
83. FIr(acac) [G]
Iridium(Ⅲ) bis[4,6-di-fluorophenyl)-pyridinato-N,C2'](acetyl acetonate)
84. Ir(ppz)3 [B]
tri(1-phenylpyrazolato)iridium
85. o-TTA [B]
tri (o-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
86. p-TTA [B]
tri (p-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
87. m-TTA [B]
tri (m-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
88. Tb(acac)3phen
tri-(2,4-pentanediono)-1,10-phenanthroline terbium(III)
<발광 호스트 재료>
1. CBP
4,4¡¯- N-N¡¯-dicarbazole-biphenyl
2. BeBq
bis(10-hydroxybenzo[h]qinolato)beryllium
3. OXD7
1,3-bis(N,N-t-butyl-phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
4. TAZ
3-phenyl-4-(1'-naphthyl)-5-phenyl-1,2,4-triazole
5. BCP
2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenantroline
6. TPBI
2,2',2"-(1,3,5-benxenetriyl)tris-[1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazole]
7. TCTA
4,4',4"-tris(N-carbazolyl)triphenylamine
8. niBr
N-2,6-dibromophenyl-1,8-naphthalimide
9. Bphen
4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline
10. CDBP
4,4'-bis(9-carbazolyl)-2,2'-dimethyl-biphenyl
<전자 저지(억제) 재료>
1. Ir(ppz)3 [B] tri(1-phenylpyrazolato)iridium
<정공 수송 재료>
1. TPD
N, N'-diphenyl-N, N'-bis(3-methylphenyl)1-1' biphenyl-4,4'-diamine
2. ¥á-NPD
(N,N'-di(naphthalene-1-yl)-N,N'-diphenyl-benxoidine
3. m-MTDATA
4,4',4"-tris(N-(3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenyl-amine)triphenylamine
4. PBD
2-biphenyl-4-yl-5-(4-t-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
5. NPD
N, N'-diphenyl-N, N'-di(1-napthl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine
6. PPD
7. TTBND
8. BFA-1T
9. p-dmDPS
10. pTDATA
11. TDAB
12. TDAPD
13. p-DPA-TDAB
1,3,5-tris[N-4-diphenylaminophenyl) phenylamino]benzene
14. β-NPD
15. CBP
4,4¡¯- N-N¡¯-dicarbazole-biphenyl
16. BMA-nT
17. TBA
18. o-TTA
tri (o-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
19. p-TTA
tri (p-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
20. m-TTA
tri (m-terphenyl-4-yl) amine
21. Spiro-TPD
Spiro-N, N'-diphenyl-N, N'-bis(3-methylphenyl)1-1' biphenyl-4,4'-diamine
22. TPTE
23. TCTA 4,4',4"-tri(N-carbazolyl) triphenylamine
24. 1-TNATA
4,4',4"-tris[1-naphthyl(phenyl)amino]triphenylamine
25. 2-TNATA
4,4',4"-tris[2-naphthyl(phenyl)amino]triphenylamine
26. p-PMTDATA
4,4',4"-tris[biphenyl-4-yl-(3-methylphenyl)amino]triphenylamine
27. TFATA
4,4',4"-tris[9,9-dimethyl-2-fluorenyl(phenyl)amino]triphenylamine
28. TCTA
4,4',4"-tris(N-carbazolyl)triphenylamine
<정공 주입 재료>
1. CuPc
copper phthalocyanine
2. m-MTDATA
4,4',4"-tris(N-(3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenyl-amine)triphenylamine
3. TDATA
4,4',4"-tris(N,N-diphenyl-amino)triphenylamine
4. F4 -TCNQ
tetrafluoro-tetracyano-quinodimethane
5. TF-TCNQ
tetra(fluoro)-tetra(cyano)quino-dimethane
6. TBPAH
tris(4-bromophenyl)aminium hexachloroantimonate
7. DEtDOc6T
8. TCTA
4,4',4"-tris(N-carbazolyl)triphenylamine
9. p-DPA-TDAB
1,3,5-tris[N-4-diphenylaminophenyl) phenylamino]benzene
10. m-MTDAPB
1,3,4,-tris{4-[methylphenyl (phenyl) amino] phenyl} benzene
11. 1-TNATA
4,4',4"-Tris(N-(1-naphthyl)-N-phenyl-amino)-triphenylamine
12. 2-TNATA
4,4',4"-Tris(N-(2-naphthyl)-N-phenyl-amino)-triphenylamine
흡습제
13. BaO barium oxide,
유기 EL 소자를 봉지할 때 넣는 흡습제
봉지재
전극 재료
1. ITO indium-tin-oxide
2. IZO indium-Zinc-oxide
3. Cs Cesium
4. Li Lithium
5. Ca Potassium
6. Al aluminium
7. Cu Copper
8. Ag
Siver Terms related with performances and specifications
1. 가속계수(acceleration coefficient)
가속 시험으로부터 실제 수명을 예측하는데 사용되어지는 계수
2. 가속계수표(acceleration table)
각각의 환경적 인자에 대한 가속계수를 표의 형태로 표시한 것
3. 가속시험(acceleration test)
실제 사용 조건에서의 수명 측정에는 오랜 시간이 요구되므로 동작조건(전압, 전류)이나 환경조건(온 도, 습도 등)을 높은 조건하에서 수명을 측정하여 실제 수명을 예측하는 시험. 즉, 시험 시간을 단축 할 목적으로 기준보다 가혹한 조건에서 실시하는 시험
4. acceptable reliablity level (ARL)
acceptable reliablity level의 약어로, 고장률의 상한을 의미
5. 종횡비(aspect ratio)
Ratio of display width to display height; for example 4:3, 16:9
6. 흑점(암점)(black spots (or dark spots))
non-emitting area of the pixel or the display panel, caused by pinholes in the cathode metal, and ingress of water/oxygen, etc.
7. 브릿지(bridge)
Lead와 Lead 사이에 Solder가 연결되어 Short 되어있는 형태.
8. 휘도가속시험(brightness acceleration test)
휘도를 기준으로 하여 실제 평균동작 휘도보다 높은 조건으로 수명을 측정
9. 칼슘테스트(calcium test)
encapsulation 정도를 평가위한 수단으로서, 내부에 calcium의 pattern을 형성하여, 이의 산화정도로 서 수분 차단 효과를 확인하기 위한 실험
10. 정전용량측정(capacitance-voltage (C-V)
measurements) measurements used to determine several parameters of semiconductor materials and structures such as density of traps, width of the depletion layer, etc..
11. 음극산화(cathode oxidation)
수분 및 산소분위기 하에서 음극이 산화되는 것을 칭함.
12. CIE 색좌표(CIE chromaticity coordinates (CIE coordinates))
Proportions of standard primaries(tristimulus values) required for a color match: ratios of each tristimulus value of a color to their sum
색상 일치에 필요한 표준 원색(삼자극값)의 비율: 색상의 각 삼자극값과 그 합의 비율
13. color change material(color change efficiency drop)
CCM 물질을 사용한 제품의 경우 CCM 내부에 혼재하여 있는 flourescence의 변환 효율이 저하되는 것을 나타냄. (기타재료 분류)
14. 색수(color number)
maximum number of colors in a display
15. 색순도(color Purity)
CIE 좌표계에서 NTSC좌표로 형성되는 삼각형의 면적대비 RGB 세점으로 구성된 삼각형의 면적비를 의미하는 것으로, 이의 수치가 높을 수록 선명한 색이 재현됨을 의미한다.
16. 색재현율(color gamut)
17. 복합환경시험(complex environment test)
환경시험, 내구성 시험, 수명 시험등을 복합적으로 동시에 수행하는 시험방식
18. 명암대비(contrast ratio (C/R))
Ratio of the highest luminance (brightest) to the lowest luminance; C/R=(Luminance with all Pixels white)/(Luminance with all Pixels black)
19. 크로스토크(crosstalk)
a problem that the unselected pixel emits light due to the leakage current between a selected and unselected pixel .
20. 전류가속시험(current driving acceleration test)
전류를 기준으로 하여 실제 평균 동작 전류 보다 높은 조건으로 수명을 측정,신뢰성 평가를 위하여 전류에 대하여 가혹한 조건을 가하는 것으로, 유기 발광 소자에서는 전류와 휘도는 비례관계를 가지 기 때문에 휘도 가속 이라고도 함.
21. 전류-전압 측정(current-voltage (I-V) measurements)
measurements used to determine the electrical characteristics of semiconductor devices by measuring current flowing across the device as a function of applied voltage.
22. 직류전류가속시험(DC driving acceleration test)
전류가속시험에서 DC 전류를 사용하여 구동하며 수명을 측정하는 방법
23. 결함(Defect)
A point or a part in a device that shows undesirable operation characteristics; a general term including point defect, line defect, cross-talk, white spot, dark spot
24. 대각 크기(diagonal size)
Length of display diagonal
25. DPI(dot per inch (dpi))
number of dots per inch
26. 화소 간격(pixel pitch)
a distance between the nearest pixels of the same color in a display
27. 부화소간격(sub-pixel pitch)
28. 내구성 시험(durability test)
여러 가지 조건으로 반복적으로 수행하여 어느 기간까지 견딜 수 있는 가를 시험하는 것
29. 전기시험(electric test)
제품의 전기적 특성이 제품사양을 만족하는지를 평가하는 시험으로, 접지연속성, 전압 margin, 주파수 margin, timing margin, 소비전력, inrush current, power sequence, on/off 시험, E.S.D 시험
30. 계조표시(gray scale)
An intermediate luminous level of light, between "full on" and "full off," that penetrates a color filter primary. Display is said to have gray scale capability if it can display images providing more than two luminance levels.
컬러 필터 기본을 통과하는 "전체 켜짐"과 "완전 꺼짐" 사이의 중간 광도 수준입니다. 디스플레이는 2개 이상의 휘도 레벨을 제공하는 이미지를 표시할 수 있는 경우 그레이 스케일 기능이 있다고 합니다.
31. 고온고습동작시험(high temperature & high humidity operation test)
50℃, 80%RH 이상의 고온 고습 환경 조건에서 연속 동작하여 동작특성을 측정하는 시험
32. 고온고습보관시험(high temperature & high humidity storage test)
50℃, 80%RH 이상의 고온 고습 환경 조건에서 동작하지 않는 상태로 일정 기간 방치하고 동작특성 변화를 측정하는 시험
33. 고온동작시험(high temperature operation test)
50℃ 이상의 고온 환경 조건에서 연속 동작하여 동작특성을 측정하는 시험
34. 고온보관시험(high temperature storage test)
50℃ 이상의 고온 환경 조건에서 동작하지 않는 상태로 일정 기간 방치하여 동작특성 변화를 측정하 는 시험
35. 습도가속시험(humidity acceleration test)
신뢰성 평가를 위하여 상대 습도 환경에 대하여 가혹한 조건을 가하는 것
36. 화질평가(image evaluation)
제품의 신뢰성에 영향을 미칠 우려가 있는 화면품질 유/무를 평가하는 시험으로, function 불량, panel 불량, EL 자체의 불량 등을 검사 및 평가하는 시험을 칭함
37. 선결함(line defect)
동일한 Line을 따라 Defect이 발생하는 현상. 유기 발광 소자를 구동하기 위해 사용하는 액티브형의 경우 line 자체의 open등에 의해서 발생하여, 디스플레이 구동 시 라인상의 불량을 나타낸다.
38. 신간균일도(line to line uniformity)
스트라이프 형상으로 배치된 각 부화소별 간의 균일도를 나타내는 것
39. 저온동작시험(low temperature operation test)
0℃ 이하의 저온 환경 조건에서 연속 동작하여 동작특성을 측정하는 시험
40. 저온보관시험(low temperature storage test)
0℃ 이하의 저온 환경 조건에서 동작하지 않는 상태로 일정 기간 방치하여 동작특성 변화를 측정하는 시험
41. 기구시험(mechanical test)
제품의 보관, 운송, 조립 및 최종 사용자의 사용/취급 환경에서의 신뢰성을 평가하는 시험으로 진동/ 충격 및 포장/낙하 시험 등을 칭함.
42. 무라(mura)
anomalous non-uniformity of the reproduced image (3.146 in 47C/262/CD 61988-1/Ed1-2CD)
재생산된 이미지의 비정상적인 불균일
43. 일계조전류값(one gray current level)
유기 전계 소자의 구동에 필요한 최소 전류와 최대 전류의 차에 구동용으로 필요한 gray수로 나눈 값
44. 동작수명(operatiion lifetime)
연속 동작상태에서 동작특성이 요구조건 이하로 떨어지는데 걸리는 시간.
45. 전기광학시험(optoelectric test)
제품의 전기광학적 특성이 제품사양을 만족하는지를 평가하는 시험으로, 휘도, flicker,응답속도, crosstalk, 색좌표 및 색온도, 시야각, contrast ratio, 휘도 균일도, gray scale 등을 평가함.
46. 최대휘도(peak luminance)
maximum luminance of a pixel or screen of the display
47. 화소 축소(pixel shrinkage)
pixel이 70%로 줄어드는데 걸리는 시간
48. 점결함(point defect)
a defect in the image reproduction that appears less brightness than the correct image (3. 52 dark defect in 47C/262/CD 61988-1/Ed1-2CD)
49. 소비전력(power consumption)
유기 전계 발광 소자의 발광에 필요한 전력의 총칭으로서, 발광에 필요한 구동 회로부의 소비전력과 발광 소자 자체에서 소비된 전력의 합산으로 이루어짐.
50. 펄스전류가속시험(pulse driving acceleration test)
전류가속시험에서 pulse 전류를 사용하여 구동하며 수명을 측정하는 방법
51. 신뢰성시험(reliability test)
제품의 신뢰성을 향상하기 위해서 행해지는 시험의 총칭을 의미하며, 시스템, 기기, 부품 등의 신뢰도 를 평가, 해석하기 위한 시험
52. 잔상(Residual image)
표시가 변할 때, 앞의 정보가 사라지지 않고 남아 있다가 시간이 경과함에 따라 소멸된다. 앞의 정보 가 소멸되지 않고 남아 있을 때의 이미지를 의미함.
53. 응답시간(response time)
디스플레이가 on/off 될 때 걸리는 시간.
54. 상온동작시험(room temperature operation test)
25℃나 35℃ 실온 환경 조건에서 연속 동작하여 동작특성을 측정하는 시험
55. 거칠기(roughness)
lack of planarity of solid surface at the atomic level; surface roughness is measured as a difference between highest and deepest surface features.
원자 수준에서 고체 표면의 평면성 부족; 표면 거칠기는 가장 높은 표면 기능과 가장 깊은 표면 기능 간의 차이로 측정됩니다.
56. 단락(short)
Device의 단자 또는 Line간에 또는 절연되어야 할 부분이 공정 이상에 의해 연결됨.
57. 보관수명(storage lifetime)
동작하지 않은 상태로 일정 환경조건 하에서 놓아 두었을 때 동작상태가 요구조건 이하로 떨어지는 데 걸리는 시간
58. 온도가속시험(temperature acceleration test)
온도를 기준으로 하여 실제 평균 동작 온도 보다 높은 조건으로 수명을 측정
59. 열충격시험(thermal shock test)
저온에서 고온으로, 고온에서 저온으로 일정 간격 cycle로 수회 반복한 후 동작특성 변화를 측정하는 시험 (ex.-20℃ ↔ 60℃, 30/30min, 100cycle)
60. 문턱전압변화(threshold voltage shift)
외부 환경, 전압 및 전류에 의해 문턱전압의 변화의 총칭
61. 진동충격시험(vibration & shock test)
규칙적이거나 불규칙한 진동에 대한 동작상태 시험 (sine, half sine, random, truck cycle 등)
62. 외관검사(visual inspection)
제품의 신뢰성에 영향을 미칠 우려가 있는 구조적 안정성 유/무를 평가하는 시험으로 각각의 치수/무 게/두께 및 포장 검사, assembly 상태 검사 등을 칭함
63. 백색균형변화(white balance shift)
유기 전계 소자의 경우, 적색·녹색·청색의 구동 시간에 따른 휘도 저하가 다름으로 인하여, 초기와 일 정 시간 경과후의 백색 균형이 변화하게 된다. 이 변화하는 정도를 나타냄.
64. 백색균일도(white chromaticity uniformity)
the chromatic uniformity of a full white screen at the prescribed sampling points (expressed as the difference in chromatic coordinates) (3.231 in 47C/262/CD 61988-1/Ed1-2CD)
지정된 샘플링 지점에서 전체 흰색 화면의 색 균일도(색 좌표의 차이로 표시)
65. 휘도균일도(brightness uniformity)
66. 명점(백점)(white spot)
발광되는 다른 부위보다 더욱 밝게 나타나는 부분
67. 시감효율(Luminous efficiency)
시감효율이라 하며 사람의 눈에 보이는 밝기 효율
68. 색변이(color shift)
열화에 의한 색(색좌표)의 변화
'비지니스 & 기술 > OCA & Film' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OLED vs. QLED, Mini-LED (1) | 2024.01.13 |
|---|---|
| CFRP (탄소섬유강화플라스틱) (0) | 2022.10.15 |
| Fold-able Phone 주요 부품과 업체 (0) | 2022.10.14 |
| CPI & UTG, Polyimide (0) | 2022.10.14 |
| Optical Physics (2) | 2022.10.14 |